EyeRounds Online Atlas of Ophthalmology
Contributor: William Charles Caccamise, Sr, MD, Retired Clinical Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry
*Dr. Caccamise has very generously shared his images of patients taken while operating during the "eye season" in rural India as well as those from his private practice during the 1960's and 1970's. Many of his images are significant for their historical perspective and for techniques and conditions seen in settings in undeveloped areas.
Category: Cornea
Cornea: corneal abrasion with reflex spastic miosis
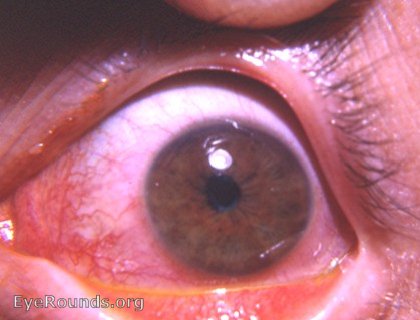
The cornea shows an abrasion above the light reflex. There is a spastic miosis due to an antidromic reflex that travels to the iris from the irritated cornea by way of the trigeminal nerve. An iritis is already evident in the photo: there is spastic miosis and some inflammatory exudate is already visible on the inferior pupil margin. This explains the basis of photophobia in an eye with a corneal abrasion even though the cornea is totally insensitive to light 1. the cornea is abraded 2. Antidromic impulses from the irritated trigeminal nerve fibers in the cornea travel to the iris 3. These impulses initiate a reaction in the iris with dilation and leakage of bloodvessels and a spastic miosis 4. the exposure of the injured eye to light produces a photophobia even though both the cornea and the iris are insensitive to light. The photophobia results when the light initiates a pupillary reaction in a congested iris with a resultant iritation of iris nerve fibers. Dilating the pupil with cycloplegics provides the patient relief by immobilizing the pupil in a dilated state - thus providing relief from pupil reaction to light. Photophobia is the unpleasant reaction to light. Dazzling is the unpleasant reaction to an excessive amount of light. Again, to provide relief to a patient with a corneal abrasion (or keratitis) the pupil should be immobilized by means of cycloplegics. Of course, dark sunglasses will provide additional comfort through reduced light and thus further reduction in stimuli to the pupil of the reflexly congested, irritated iris.


Ophthalmic Atlas Images by EyeRounds.org, The University of Iowa are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.


